# 2、Redux
# 目标
- Reducer
- 函数组合compose
- redux
- 常用中间件
- thunk
- logger
- promise
- combineReducers
# Reducer
Reducer 就是一个纯函数,接收旧的 state 和 action,返回新的 state。
;(previousState, action) => newState
之所以将这样的函数称之为 reducer,是因为这种函数与被传⼊ Array.prototype.reduce(reducer, ?initialValue) 里的回调函数,属于相同的类型。
保持 reducer 纯净非常重要。永远不要在 reducer 里做这些操作:
- 修改传⼊参数;
- 执行有副作用的操作,如 API 请求和路由跳转;
- 调⽤非纯函数,如 Date.now() 或 Math.random()(因为像 Date.now(),结果每次都不一样,是非纯函数)。
回忆下 reduce
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue;
// 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
console.log(array1.reduce(reducer));
// expected output: 10
// 5 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
console.log(array1.reduce(reducer, 5));
// expected output: 15
# 函数组合compose 与 柯里化currying
函数式编程有两个重要的方法,即 函数组合compose 与 柯里化currying。
# compose
思考:有如下函数,聚合成一个函数,并把第一个函数的返回值传递给下⼀个函数,如何处理呢?
function f1(arg) {
console.log("f1", arg);
return arg;
}
function f2(arg) {
console.log("f2", arg);
return arg;
}
function f3(arg) {
console.log("f3", arg);
return arg;
}
// 你当然可以这样,但这太啰嗦了,不利于维护:
f1(f2(f3("lalala")))
组合函数:如果一个值要经过多个函数,才能变成另外一个值,就可以把所有中间步骤合并成一个函数,这叫做"函数的合成"(compose)。
使用组合函数compose:
- 并不在compose中执行传入的函数,而是
- 返回一个函数,在传入参数时才执行
function f1(arg) {
console.log("f1", arg);
return arg;
}
function f2(arg) {
console.log("f2", arg);
return arg;
}
function f3(arg) {
console.log("f3", arg);
return arg;
}
function compose(...funcs) {
if (funcs.lenght === 0) {
return arg => arg
}
// 注意这里的reduce中接收的是func,所以要用双箭头,返回一个函数来接收参数
return funcs.reduce((a, b) => (...args) => a(b(...args)))
// return funcs.reduce((a, b) => {
// console.log(a, b); // f1() f2()
// return (...args) => {
// console.log("args", ...args); // lalala
// return a(b(...args));
// };
// });
}
let res = compose(f1, f2, f3)("lalala") // 等价于 f1(f2(f3("lalala")))
console.log(res)
# 柯里化
柯里化(英语:Currying),又译为卡瑞化或加里化,是把接受多个参数 (opens new window)的函数 (opens new window)变换成接受一个单一参数(最初函数的第一个参数)的函数,并且返回接受余下的参数而且返回结果的新函数的技术。
所谓"柯里化",就是把一个多参数的函数,转化为单参数函数。
// 柯里化之前
function add(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
add(1, 2) // 3
// 柯里化之后
function addX(y) {
return function (x) {
return x + y;
};
}
addX(2)(1) // 3
这样调用上述函数:(foo(3))(4),或直接foo(3)(4)。
看下面的例子,这里我们定义了一个 add 函数,它接受一个参数并返回一个新的函数。调用 add 之后,返回的函数就通过闭包的方式记住了 add 的第一个参数。一次性地调用它实在是有点繁琐,好在我们可以使用一个特殊的 curry 帮助函数(helper function)使这类函数的定义和调用更加容易。
var add = function(x) {
return function(y) {
return x + y;
};
};
var increment = add(1);
var addTen = add(10);
increment(2); // 3
addTen(2); // 12
# Redux原理
Redux是JavaScript应⽤的状态容器,它保证程序⾏为⼀致性且易于测试。(这里需要再强调一下:Redux 和 React 之间没有关系。Redux 支持 React、Angular、Ember、jQuery 甚至纯 JavaScript。但 Redux 与 React 搭配起来最好)。
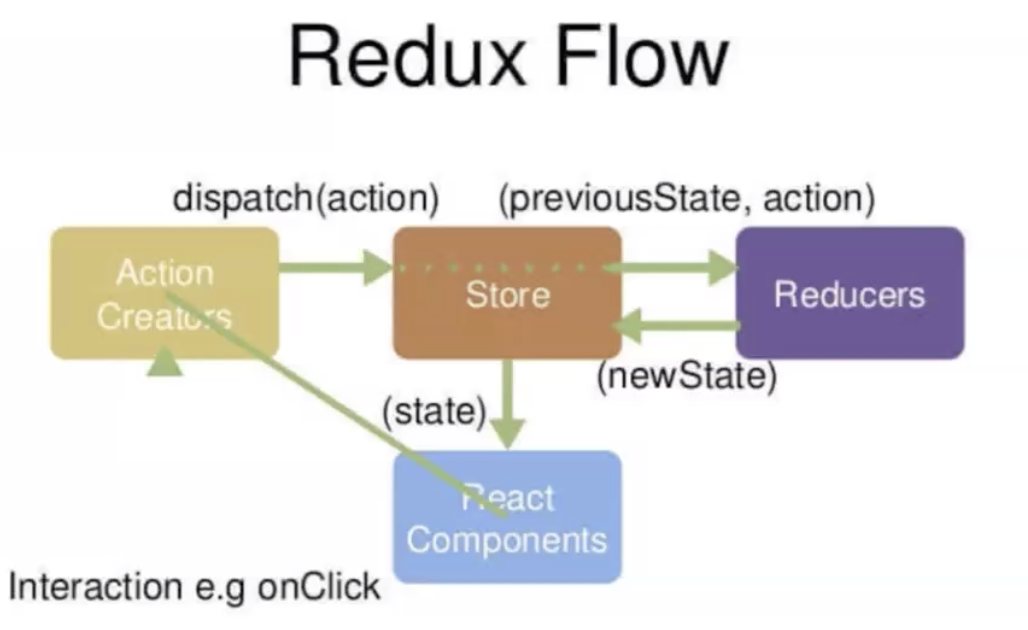
一个形象的比喻,假设有一家公司Redux:
Store:公司财务部门,统一管钱- 从审批部门拿到账单action后,将之前的账目state和账单action都使用Reducers的处理规则处理
- 从Reducers得到新的账目newState后,给到对应的业务部门React Components
React Components:公司各业务部门- 要用钱时,需要向审批部门Action Creators提申请
Action Creators:审批部门- 公司各业务部门提申请给审批部门后
- 审批部门dispatch一个action账单给Store
Reducers:处理钱的规则- 定义账目state的修改规则
- 从Store拿到账单action和原有账目state
- 处理得到新的账目newState,给回到Store财务部门
总结一下:
- 需要⼀个store来存储数据;
- store⾥的reducer初始化state并定义state修改规则;
- 通过dispatch⼀个action来提交对数据的修改;
- action提交到reducer函数⾥,根据传⼊的action的type,返回新的state;
# 实现自己的Redux
# 基础实现
- store/index.js
import { createStore } from "../InchRedux";
function countReducer(state = 0, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "ADD":
return state + 1;
case "MINUS":
return state - action.payload || 1;
default:
return state;
}
}
const store = createStore(countReducer);
export default store;
- ReduxPage.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
import store from "../store/";
export default class ReduxPage extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
this.forceUpdate();
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this.unsubscribe) {
this.unsubscribe();
}
}
add = () => {
store.dispatch({ type: "ADD" });
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>ReduxPage</h3>
<p>{store.getState()}</p>
<button onClick={this.add}>add</button>
</div>
);
}
}
- InchRedux/createStore
export default function createStore(reducer) {
let currentState
let currentListeners = []
// 获取状态
function getState() {
return currentState
}
// 修改状态
function dispatch(action) {
// 更新状态
currentState = reducer(currentState, action)
// 通知组件,找到订阅并触发
currentListeners.forEache(listener => listener())
}
// 订阅状态
function subscribe(listener) {
currentListeners.push(listener)
// 返回取消订阅函数
return () => {
const index = currentListeners.indexOf(listener)
currentListeners.splice(index, 1)
}
}
// 解决没有初值的问题,手动执行一次dispatch,使其走到switch default的path
dispatch({ type: "lsfdlsflsflseifieiiii2ii23i23i" }) // 随便给个不会匹配的type即可
return {
getState,
dispatch,
subscribe
}
};
# 增加异步action实现
Redux只是个纯粹的状态管理器,默认只⽀持同步action,即action必须是对象(plain object)。要实现异步action,比如延迟,⽹络请求,就需要中间件的支持,⽐如使⽤最简单的redux-thunk和redux-logger。另外对于promise的异步支持,需要使用redux-promise。
中间件就是⼀个函数,对 store.dispatch ⽅法进行改造,在发出 Action 和执⾏ Reducer 这两步之间,添加其他功能。
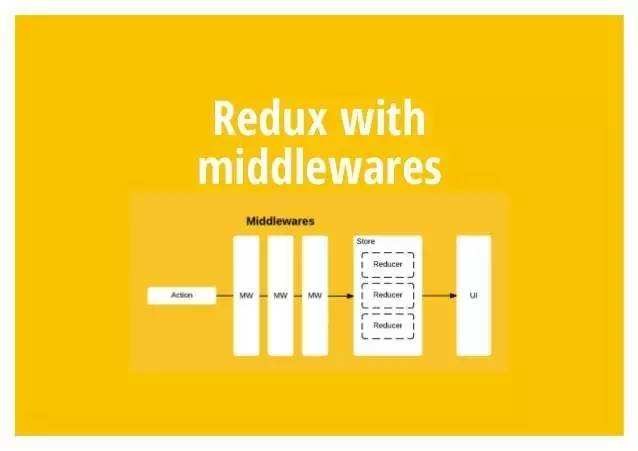
# 如何使用中间件
// import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "../InchRedux";
// import logger from "redux-logger";
import logger from "../InchRedux/logger";
// import thunk from "redux-thunk";
import thunk from "../InchRedux/thunk";
// import promise from "redux-promise";
import promise from "../InchRedux/promise";
function countReducer(state = 0, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "ADD":
return state + 1;
case "MINUS":
console.log(state, action.payload)
return state - action.payload || 1;
default:
return state;
}
}
const store = createStore(countReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk, promise, logger)); // 注意将logger放到最后
export default store;
- ReduxPage.js
addAsync = () => {
store.dispatch((dispatch, getState) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(getState())
dispatch({ type: "ADD" })
}, 1000)
})
}
promiseMinus = () => {
store.dispatch(
Promise.resolve({
type: "MINUS",
payload: 100
})
);
};
# 中间件实现
# 实现applyMiddleware
- 首先升级下createStore,需要接收第二个参数enhancer,即应用的中间件,对dispatch进行增强:
export default function createStore(reducer, enhancer) {
if (enhancer) {
// 增强createStore的dispatch
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer)
}
// ...
}
- 核⼼任务是实现函数序列执行,即 applyMiddleware.js:
export default function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
return createStore => reducer => {
const store = createStore(reducer)
// 缓存原dispatch
let dispatch = store.dispatch
const midApi = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: action => dispatch(action)
}
// 加强dispatch,使用compose将dispatch和中间件函数都执行
const middlewareChain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(midApi))
dispatch = compose(...middlewareChain)(store.dispatch)
// 返回store,同时把dispatch加强
return {
...store,
// 返回加强版的dispatch
dispatch
}
}
};
function compose(...funcs) {
if (funcs.length === 0) {
return arg => arg
}
return funcs.reduce((a, b) => (...args) => a(b(...args)))
}
# 实现redux-thunk
处理异步:
function thunk({dispatch, getState}) {
return next => action => {
if (typeof action === "function") {
return action(dispatch, getState)
} else if (typeof action === "object") {
return next(action)
}
}
}
# 实现redux-logger
打印日志:
function logger({dispatch, getState}) {
return next => action => {
console.log("**************************************")
// prev state
const prevState = getState()
console.log("prev state", prevState)
const returnVal = next(action)
// next state
const nextState = getState()
console.log("next state", nextState)
console.log("**************************************")
return returnVal
}
}
# 实现redux-promise
支持promise:
import isPromise from 'is-promise';
export default function promise({ dispatch }) {
return next => action => {
return isPromise(action) ? action.then(dispatch) : next(action);
};
};
# combineReducers
# combineReducers使用
在应用中,不可能只有一个reducer,面对多个reducer,redux提供了combineReducers,合并多个reducer,使用方式:
function countReducer(state = 0, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "ADD":
return state + 1;
case "MINUS":
return state - action.payload || 1;
default:
return state;
}
}
function countReducer2(state = {num: 0}, {type, payload}) {
switch (action.type) {
case "ADD2":
return {...state, num: state.num + payload};
default:
return state;
}
}
const store = createStore(
combineReducers({
count: countReducer,
count2: countReducer2
}),
applyMiddleware(thunk, promise, logger)
);
export default store;
在访问时:
<p>{store.getState().count}</p>
<p>{store.getState().count2.num}</p>
# 实现combineReducers
export default function combineReducers(reducers) {
return function combination(state = {}, action) {
let nextState = {}
let hasChanged = false
for (let key in reducers) {
const reducer = reducers[key]
nextState[key] = reducer(state[key], action)
hasChanged = hasChanged || nextState[key] !== state[key]
}
hasChanged = hasChanged || Object.keys(nextState).length !== Object.keys(state).length
return hasChanged ? nextState : state
}
};
