# 数据结构-树和二叉树
树是用来模拟具有树状结构性质的数据集合。而二叉树是树最简单、应用最广泛的种类。二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构,通常将当前节点称作“根节点”,子树被称作“左子树”和“右子树”。
# 完全二叉树的一些公式
完全二叉树:除了最后一层,所有层的节点数达到最大,与此同时,最后一层的所有节点都在最左侧。(堆使用完全二叉树)
- 第n层的节点数最多为2n个节点;
- n层二叉树最多有20+...+2n=2n+1-1个节点;
- 第一个非叶子节点:length/2;
- 一个节点的孩子节点:2n、2n+1。
满二叉树:所有层的节点数达到最大。
# 二叉树的构造
二叉树有两种表示形式:链表形式 与 数组形式。
# 链表形式表示
一般情况下,二叉树都通过链表形式存储:
// 二叉树节点
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
# 数组形式表示
对于完全二叉树可以使用「层序遍历数组」表示,因为对完全二叉树而言,可以很容易通过数组下标确认相互关系,比如堆排序中使用的最大堆最小堆,就是直接利用数组模拟完全二叉树,进而构造最大(最小)堆,实现排序。
对于一般二叉树也可以使用数组表示,为表述清晰,会增加必要的null值,比如下图:
5
/ \
1 4
/ \
3 6
1
\
2
/
3
用数组表示为:[5,1,4,null,null,3,6] 、 [1,null,2,3]
注:在leetcode上做题时,一般都是给出数组表示,leetcode的测试用例会自动将其转成链表形式,但如果我们本地需要验证测试用例时,还需要自己手动转换。
# 基本结构与功能
// 二叉树节点
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
// show() {
// console.log(this.data);
// }
}
class Tree {
constructor(data = null) {
this.root = data;
}
// 基础方法:插入、遍历、深度
insert(data) {
var node = new Node(data, null, null);
if (!this.root) {
this.root = node;
return;
}
var current = this.root;
var parent = null;
while (current) {
parent = current;
if (data < parent.data) {
current = current.left;
if (!current) {
parent.left = node;
return;
}
} else {
current = current.right;
if (!current) {
parent.right = node;
return;
}
}
}
},
preOrder(node) {
if (node) {
node.show();
this.preOrder(node.left);
this.preOrder(node.right);
}
},
middleOrder(node) {
if (node) {
this.middleOrder(node.left);
node.show();
this.middleOrder(node.right);
}
},
laterOrder(node) {
if (node) {
this.laterOrder(node.left);
this.laterOrder(node.right);
node.show();
}
},
getMin() {
var current = this.root;
while (current) {
if (!current.left) {
return current;
}
current = current.left;
}
},
getMax() {
var current = this.root;
while (current) {
if (!current.right) {
return current;
}
current = current.right;
}
},
getDeep(node, deep) {
deep = deep || 0;
if (node == null) {
return deep;
}
deep++;
var dleft = this.getDeep(node.left, deep);
var dright = this.getDeep(node.right, deep);
return Math.max(dleft, dright);
}
// 将 层序遍历数组 转换成 链表形式
static toLinklistMode(data) {
let toNode = item => {
if (!item) {
return null;
} else {
return new Node(item);
}
};
let queue = [];
const root = toNode(data.shift());
queue.push(root); // 入队列第一个元素
while (data.length > 0) {
//当数组里还有项的时候就拿数组的项去填充队列
let current = queue.shift();
current.left = toNode(data.shift());
if (current.left) {
queue.push(current.left);
}
current.right = toNode(data.shift());
if (current.right) {
queue.push(current.right);
}
}
return root;
}
// 将 链表形式 转换成 层序遍历数组
static toArrayMode(root) {
let queue = [];
let list = [];
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length > 0) {
let current = queue.shift();
if (current.left) {
queue.push(current.left);
list.push(current.left.val);
} else {
list.push(null);
}
if (current.right) {
queue.push(current.right);
list.push(current.right.val);
} else {
list.push(null);
}
}
// 我们在深度优先遍历的时候将节点保存下来,如果是null也保存,完全二叉树的性质要求我们不能有null混在值中
// 拿到这个list之后
// 第一步是将最后连续的null删掉
let point = list.length - 1; // 从表最后开始看
while (list[point] === null) {
list.pop();
point--;
}
// 之后再检查list中是否还有null,如果没有就是完全二叉树,有就不是
// return list.every((item)=>{return item!==null})
return [root.val].concat(list); // 换成输出这行代码就能输出二叉树的数组表示形式,与前面的constructor方法正好相反
}
}
# 树查找
树查找
getNode(data, node) {
if (node) {
if (data === node.data) {
return node;
} else if (data < node.data) {
return this.getNode(data,node.left);
} else {
return this.getNode(data,node.right);
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
# 二分查找
二分查找的条件是必须是有序的线性表。
和线性表的中点值进行比较,如果小就继续在小的序列中查找,如此递归直到找到相同的值。
二分查找
function binarySearch(target, arr, start, end) {
if (start > end) {
return -1;
}
var mid = Math.floor((end + start) / 2);
if (target == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
} else if (target < arr[mid]) {
return binarySearch(target, arr, start, mid - 1);
} else {
return binarySearch(target, arr, mid + 1, end);
}
}
var arr = [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 6, 7, 8]
console.log(binarySearch(1, arr, 0, arr.length-1));
# 经典题目
# 1、二叉树遍历
如何遍历一棵树 有两种通用的遍历树的策略:
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)
- 在这个策略中,我们采用深度作为优先级,以便从根开始一直到达某个确定的叶子,然后再返回根到达另一个分支。
- 深度优先搜索策略又可以根据根节点、左孩子和右孩子的相对顺序被细分为
先序遍历,中序遍历和后序遍历。
- 宽度优先搜索(BFS)
层序遍历,按照高度顺序一层一层的访问整棵树,高层次的节点将会比低层次的节点先被访问到。
下图中的顶点按照访问的顺序编号,按照 1-2-3-4-5 的顺序来比较不同的策略。
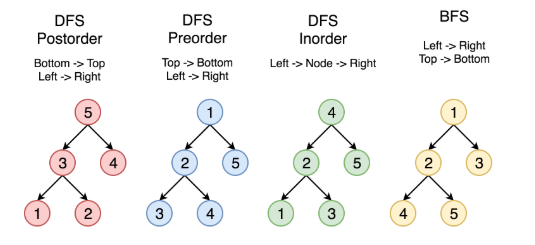
重点中的重点,最好同时掌握递归和非递归版本,递归版本很容易书写,但是真正考察基本功的是非递归版本。
# 2、二叉树的对称性
# 3、二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树是特殊的二叉树,考察二叉搜索树的题目一般都是考察二叉搜索树的特性,所以掌握好它的特性很重要。
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
# 4、二叉树的深度
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
平衡二叉树:左右子树深度之差大于1。
← [基本]复杂链表的复制 二叉树的中序遍历 →
