链表练习题集合:1、从尾到头打印链表;2、删除链表中重复的结点;3、合并两个有序链表;4、反转链表;5、链表中倒数第k个结点;6、两个链表的第一个公共结点;7、链表中环的入口结点;8、复杂链表的复制;
构建基础链表及功能:
class Node constructor (value, next) { this .value = value this .next = next } } class List constructor () { this .head = new Node(null , null ) } find(index) { let current = this .head for (let i = 0 ; i < index; ++i) { current = current.next } return current; } insert(value, index) { const prev = this .find(index) const next = new Node(value, prev.next) prev.next = next } }
从尾到头打印链表 1、题目描述 输入一个链表,按链表值从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
2、思路 (三种方法:借助栈、递归、列表的首位插入)
从头到尾打印链表比较简单,从尾到头很自然的可以想到先将链表进行反转,然后再打印。但是,通常我们不希望改变原链表的结构,这是一个只读操作 。
进一步分析,这是一个典型的“后入先出”的思想,因此很自然的可以想到用栈来实现 ,每遍历一个结点,可以将其压入栈中,遍历结束后再逐个弹栈,将结点值存入ArrayList,这样就实现了从尾到头的打印。
更进一步,既然想到了用栈,那一定可以通过递归来实现 。每访问到一个结点,先递归输出其后的结点,再输出该结点自身即可。
另外,当我们使用Java或者python语言时,有一种比较巧妙的方法就是使用列表的插入方法,每次插入数据,都总是插入到首位 ,这样得到的List就是从尾到头的链表序列。
3、代码实现 let list = new List()list.insert('a' , 0 ) list.insert('b' , 1 ) list.insert('c' , 2 ) list.insert('d' , 3 ) list.insert('e' , 4 ) console .log(list)function printFromTailToHead (node ) node.next && printFromTailToHead(node.next) node.value && console .log(node.value) } let result = printFromTailToHead(list.head)console .log(result)
删除链表中重复的结点 1、题目描述 删除有序链表 中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5。
2、思路 删除重复结点,也就是如果当前结点和下一个结点的值相同,那么就是重复的结点,都可以被删除,为了保证删除之后的链表的连通性,在删除之后,要把当前结点前面的结点和下一个没有重复的结点链接起来,为此,程序需要记录当前的最后一个不重复结点,即程序中的pre。重点在于:一定要确保当前链接到链表中的一定是不会再重复的结点,具体见代码实现。
关于第一个结点如果重复怎么办的问题,我们不用单独考虑,可以使用链表中一贯的做法,加一个头结点即可。
3、代码实现 function deleteDuplication (pHead ) if (pHead === null || pHead.next === null ) { return pHead; } var dummy = new Node(null , null ); dummy.next = pHead; var pre = dummy; var cur = pHead; while (cur !== null && cur.next !== null ) { if (cur.next.val === cur.val) { var curRepetitiveVal = cur.val; while (cur !== null && cur.val === curRepetitiveVal) { cur = cur.next; } pre.next = cur; } else { pre = cur; cur = cur.next; } } return dummy.next; } function deleteDuplication (pHead ) if (pHead === null || pHead.next === null ) { return pHead; } var dummy = new Node(null , null ); dummy.next = pHead; var pre = dummy; var cur = pHead; while (cur !== null && cur.next !== null ) { if (cur.next.val === cur.val) { pre = cur var curRepetitiveVal = cur.val; while (cur !== null && cur.val === curRepetitiveVal) { cur = cur.next; } pre.next = cur; } else { pre = cur; cur = cur.next; } } return dummy.next; } function duplicateDelete (list ) let pre = list; let cur = list.next; let next = cur.next; let flag = false ; while (next){ if (cur.value === next.value){ flag = true ; next = next.next; cur.next = next; } else { if (flag){ cur = next; next = cur.next; pre.next = cur; flag = false ; } else { pre = next; cur = next next = next.next; } } } }
合并两个有序链表 1、题目描述 输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的结点仍然是按照递增排序的。
2、思路 准备一个指针node,假设指向两个链表中节点的指针分别是:p1和p2。
比较p1和p2的value大小
3、代码实现 function merge (p1, p2 ) if (!p1) { return p2 } else if (!p2) { return p1 } let head = new Node() let node = head while (p1 && p2) { if (p1.value < p2.value) { node.next = p1 p1 = p1.next } else { node.next = p2 p2 = p2.next } node = node.next } if (p1) { node.next = p1 } if (p2) { node.next = p2 } return head.next; } function merge (p1, p2 ) if (!p1) { return p2 } else if (!p2) { return p1 } let head = null if (p1.value < p2.value) { head = p1 head.next = merge(p1.next, p2) } else { head = p2 head.next = merge(p1, p2.next) } return head }
反转链表 1、题目描述 输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
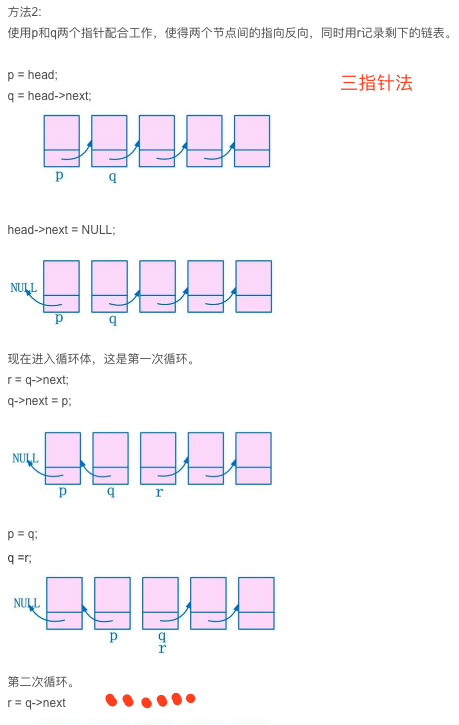
2、思路 有两种方法可以实现:(1)三指针(原地反转)。使用三个指针,分别指向当前遍历到的结点、它的前一个结点以及后一个结点。将指针反转后,三个结点依次前移即可;(2)链表头插法(注意这里是往head后插)。从第二个节点开始依次插入到第一个节点之后,最后将第一个节点挪到新表结尾;(3)递归方法。同样可以采用递归来实现反转。将头结点之后的链表反转后,再将头结点接到尾部即可。
3、代码实现 function reverseList (head ) if (head === null || head.next === null ) { return head; } let p = head let q = head.next; head.next = null ; let r; while (q) { r = q.next; q.next = p; p = q; q = r; } return p; } function reverseList (head ) if (head === null || head.next === null ) { return head; } let p = head.next let q while (p.next) { q = p.next p.next = q.next q.next = head.next head.next = q } p.next = head head = p.next.next p.next.next = null return head } function reverseList (head ) if (head === null || head.next === null ) { return head; } var new_head = reverseList(head.next); head.next.next = head; head.next = null ; return new_head; }
链表中倒数第k个结点 1、题目描述 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。为了符合习惯,从1开始计数,即链表的尾结点是倒数第1个节点。例如,一个链表有6个结点,从头结点开始,它们的值依次是1,2,3,4,5,6。则这个链表倒数第三个结点是值为4的结点。
2、思路 对于单链表来说,没有从后向前的指针,因此一个直观的解法是先进行一次遍历,统计出链表中结点的个数n,第二次再进行一次遍历,找到第n-k+1个结点就是我们要找的结点,但是这需要对链表进行两次遍历。
为了实现一次遍历,我们这里采用双指针解法(快慢指针) 。我们可以定义两个指针,第一个指针从链表的头指针开始先向前走k步,第二个指针保持不动,从第k+1步开始,第二个指针也从头开始前进,两个指针都每次前进一步。这样,两个指针的距离都一直保持在k,当快指针(走在前面的)到达null时,慢指针(走在后面的)正好到达第k个结点。注意:要时刻留意空指针的判断。
3、代码实现 function findKthFromTail (head, k ) if (!head || k <= 0 ) { return null ; } let fast = head, slow = head; for (let i = 0 ; i < k; ++i) { fast = fast.next; if (!fast) { return null ; } } while (fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; } let node3 = new Node(3 , null ), node2 = new Node(2 , node3), node1 = new Node(1 , node2), head = new Node(0 , node1); console .log(findKthFromTail(head, 2 ));console .log(findKthFromTail(head, 3 ));console .log(findKthFromTail(head, 5 ));
两个链表的第一个公共结点 1、题目描述 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
2、思路 方法一:借助辅助栈 。我们可以把两个链表的结点依次压入到两个辅助栈中,这样两个链表的尾结点就位于两个栈的栈顶,接下来比较两个栈顶的结点是否相同。如果相同,则把栈顶弹出继续比较下一个,直到找到最后一个相同的结点。此方法也很直观,时间复杂度为O(m+n),但使用了O(m+n)的空间,相当于用空间换取了时间效率的提升。
方法二:快慢指针(将两个链表设置成一样长) 。具体做法是先求出两个链表各自的长度,然后将长的链表的头砍掉,也就是长的链表先走几步,使得剩余的长度与短链表一样长,这样同时向前遍历便可以得到公共结点。时间复杂度为O(m+n),不需要额外空间。
3、代码实现 function findCommon (list1, list2 ) const stack1 = [], stack2 = []; let node = list1; while (node) { stack1.push(node); node = node.next; } node = list2; while (node) { stack2.push(node); node = node.next; } node = null ; while (stack1.length && stack2.length) { let top1 = stack1.pop(), top2 = stack2.pop(); if (top1 === top2) { node = top1; } else { break ; } } return node; } function findCommon (list1, list2 ) let length1 = 0 , length2 = 0 ; let node = list1; while (node) { ++length1; node = node.next; } node = list2; while (node) { ++length2; node = node.next; } let diff = Math .abs(length1 - length2), longList = null , shortList = null ; if (length1 > length2) { longList = list1; shortList = list2; } else { longList = list2; shortList = list1; } while (diff > 0 ) { longList = longList.next; --diff; } while (longList && shortList) { if (longList === shortList) { return longList; } longList = longList.next; shortList = shortList.next; } return null ; } const node4th = new Node(4 );const node3th = new Node(3 , node4th);const list1 = new Node(1 , new Node(2 , new Node(3 , node3th)));const list2 = new Node(5 , new Node(6 , node3th));console .log(findCommon(list1, list2));
链表中环的入口结点 1、题目描述 给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
2、思路 第一步:确定一个链表是否有环。这一步就是快慢指针法,定义两个指针,同时从链表的头结点出发,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步。如若有环,两个指针必定相遇,也就是如果快指针反追上了慢指针,说明存在环(这里要注意,两指针相遇的地方一定在环中,但不一定是环的入口),如果快指针走到了链表的末尾(指向了NULL),则说明不存在环。
第二步:找到环的入口点。这还是可以利用双指针来解决,两个指针初始都指向头结点,如果我们可以知道环中的结点个数,假设为n,那么第一个指针先向前走n步,然后两个指针(另一个从头结点开始)同时向前,当两个指针再次相遇时,他们的相遇点正好就是环的入口点。
3、代码实现 function detectCycle (head ) let fast = head, slow = head, firstMeet = null while (slow && fast && fast.next) { slow = slow.next fast = fast.next.next if (slow === fast) { firstMeet = slow break } } if (!firstMeet) { return null } while (firstMeet && head) { if (firstMeet === head) { return head } firstMeet = firstMeet.next head = head.next } return null }